LONDON: The House of Saud took the first steps on the long road to nationhood in 1727, when Imam Mohammed bin Saud succeeded his cousin, Zaid bin Markhan, as ruler of the city state of Diriyah.
It is this pivotal moment, recognized as the date when the First Saudi State came into being, that is celebrated in the Kingdom on Feb. 22 each year as Founding Day.
Imam Mohammed had learned the art of politics at his father’s side. He played a significant role in supporting him throughout his reign and proved his mettle as a leader when Diriyah was attacked in 1721 by the Banu Khalid tribe of Al-Ahsa.
Imam Mohammed led his father’s forces to victory, strengthening Diriyah’s regional standing in the process.
After the death of his father in 1725, Imam Mohammed pledged his support to Markhan of the Watban clan of the tribe Zaid, and after he emerged victorious served him loyally until the prince’s short reign was ended by an assassin the following year.
From the outset, unity was Imam Mohammed’s dream, as the official history published by the Diriyah Gate Development Authority attests.
Contemporary Arab chroniclers recorded that “the people of Diriyah were fully confident in his abilities and (that) his leadership qualities (would) free the region of division and conflict.”
Imam Mohammed was already known for “his many personal characteristics, such as his devotion, goodness, bravery, and ability to influence others,” and the passing of power to him was “a transformative moment, not only in the history of Diriyah, but in the history of Najd and the Arabian Peninsula.”
Already renowned as a man of action, Imam Mohammed would also prove himself to be a wise leader.
Imam Mohammed set about the daunting task of achieving political unity among the tribes, with the ultimate aim of establishing a greater Arabian state. (Sotheby’s)
Imam Mohammed set about the daunting task of achieving political unity among the tribes, beginning with the neighboring towns of Najd, with the ultimate aim of establishing a greater Arabian state.
As the official history published by the Diriyah Gate Development Authority attests, “it wasn’t an easy task,” but by the time of his death in 1765, Imam Mohammed bin Saud had laid the foundations for the greatest political entity central Arabia had ever seen.
From the day of his ascension, “he began planning to change the prevailing status quo of that day and time, laying down a new path in the region’s history toward unity, education, the spread of culture, enhanced communication between members of society, and perpetual security.”
Over the next nine decades, the power and influence of Diriyah grew, as the great task of unity was handed on to Mohammed’s three successors — his son Abdulaziz, who would found the royal district of At-Turaif, Abdulaziz’s son Saud the Great, under whose direction the authority of the First Saudi State reached its peak, extending over most of the Arabian Peninsula and, upon his death in 1814, his son Abdullah, who was known to be great warrior.
But challenging the vast and aggressive Ottoman empire for control of Makkah and Madinah would prove to be Diriyah’s undoing. Imam Abdullah inherited the wrath of Istanbul, which dispatched a vast force to end the threat Diriyah posed to Ottoman authority in Arabia.
It took far longer than the Sultan could have imagined. Fighting a series of fierce battles over several years against impossible odds, the Arabs were slowly driven back from the Red Sea coast to their last stand before the walls of Diriyah.
After a six-month siege, Diriyah fell. Imam Abdullah was taken as a prisoner to Istanbul, where he was executed.
Undeterred, the Second Saudi State sprang up from the rubble of the first, this time in Riyadh — the ancient capital of the Hajer Al-Yamamah region, where it thrived from 1824 to 1891.
This, too, would fall.
But among the members of the family ousted from Riyadh in 1891 by the rival House of Rashid was the 16-year-old son of the last Imam of the Second Saudi State, a young man destined to take the last great step on the path upon which his predecessor Imam Mohammed had embarked generations before.
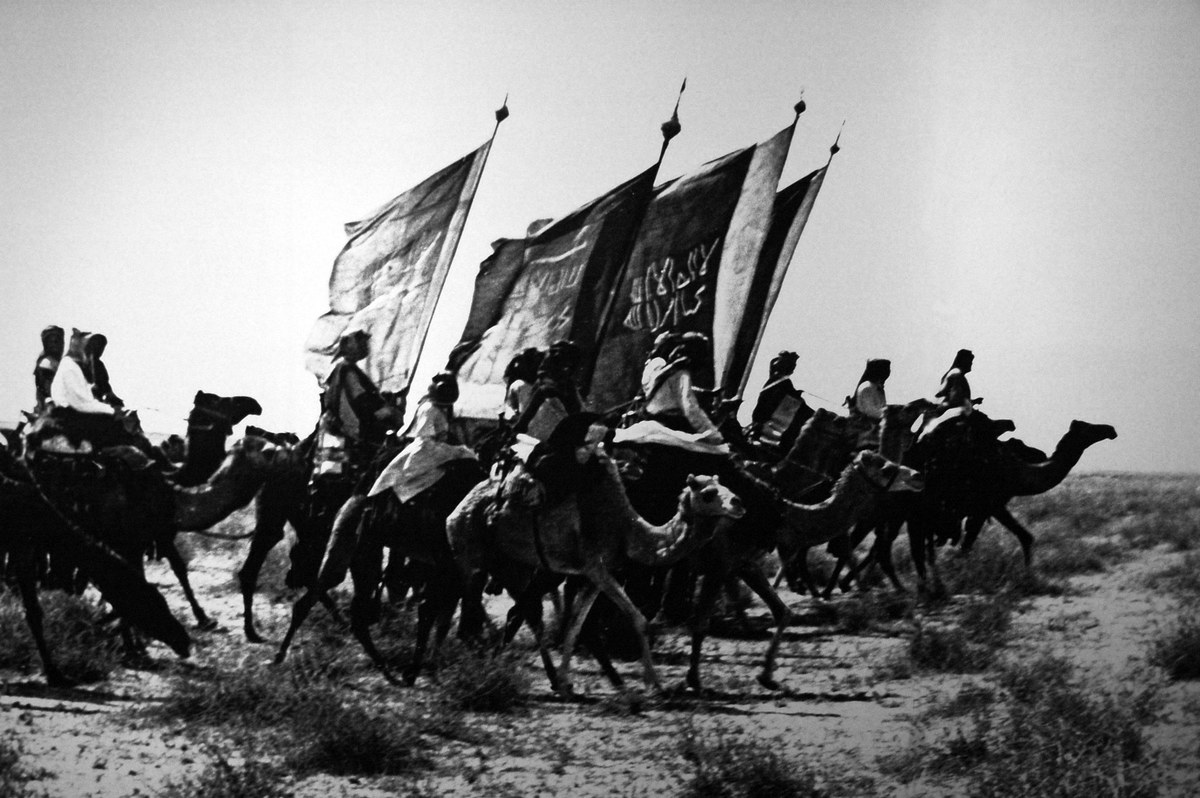

Above, warriors of Prince Abdulaziz ibn Abdul Rahman Al-Saud on camel back in Nejd, on their way to recapture Riyadh, c. 1910. (Alamy)
The story of how Prince Abdulaziz ibn Abdul Rahman Al-Saud and a small band of warriors recaptured Riyadh in 1902, restoring the House of Saud to its rightful home in the Nejd, is well known to every schoolchild in Saudi Arabia.
But Abdulaziz’s most remarkable achievement — the bringing together of the many tribes of Arabia to make possible the foundation in 1932 of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia — would require decades of unwavering dedication to his ancestor’s vision of unity.
Today, familial attachment to one or other of the tribes rooted deep in the history of the Arabian Peninsula remains a source of great pride for many Saudis and their families, and part of the fabric of the country’s diverse but unifying heritage.
This was, however, not always the case, as John Duke Anthony, founding president and chief executive of the Washington-based National Council on US-Arab Relations, noted in 1982.
“For much of Arabian history, most of these tribes existed as independent political entities in microcosm,” he wrote in an essay “Saudi Arabia: From tribal state to nation-state.”
“As such, they were capable of uniting for common action. At the same time, however, they more often than not acted as divisive forces in any larger societal context.
“It was this latter characteristic as much as any other attribute that prompted the late King Abdulaziz, the founder of modern Saudi Arabia, to seek a number of means by which he could integrate the various tribes into the new national political structure of the Kingdom.”
It was, added Anthony, “the religious content of Abdulaziz’s message as he set about knitting Arabia into a single state (that) proved to be his greatest source of strength.
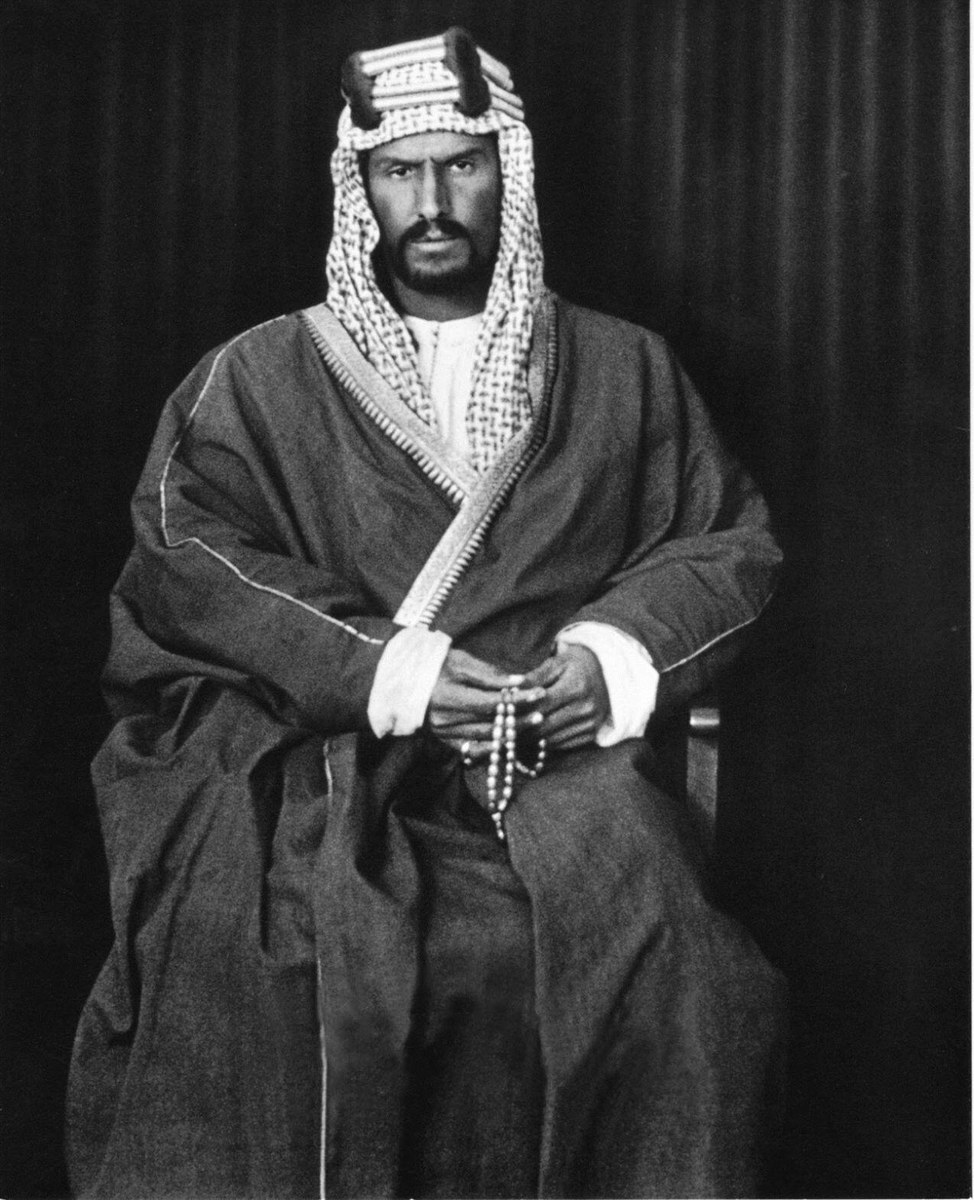

Above, Prince Abdulaziz ibn Abdul Rahman Al-Saud in Kuwait, circa 1910. (Alamy)
“He was able to direct and control a strict adherence to Islamic doctrines and, in this manner, affect a significant modification of the tribal distinctions which formerly had divided the realm.”
In 2022, Hasan Massloom, a member of the Shoura Council of Saudi Arabia, wrote that in the modern Saudi Arabia tribalism complemented rather than contradicted the Kingdom’s Vision 2030 ambitions, which were unveiled to Saudi citizens and the world by Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman in 2016.
“No discussion of social change is conceivable without acknowledging the tribal background of the society of Saudi Arabia,” Massloom wrote in an op-ed piece for Arab News.
“Tribalism in Arabia has existed for thousands of years, predating Judaism, Christianity and Islam. It was an independent, cohesive system for survival in the desert that provided social status, economic advantage and physical protection for its members.
“People of one tribe shared a common ancestry, a collective dignity and a coalesced reputation. Harsh life in the arid desert decreed a firm and binding moral bond among tribes to defend their progeny and possessions. Tribal history prided itself on social hierarchy, an obligation for vengeance and a deep commitment to territory, pasture and water wells.”
King Abdulaziz, he continued, had “tactfully pivoted the Arabian tribal scene toward his dream of a national kingdom when he persuaded hostile and fighting tribes to cast their conflicts aside and unite under his leadership to build a modern state.”
Indeed, Abdulaziz, the man known to the wider world simply as Ibn Saud, had completed the journey begun by the founding of the First Saudi State by Imam Mohammad in 1727.
On Jan. 27, 2022, Founding Day was established by a Royal Order of King Salman in recognition of this pivotal moment in the nation’s history, and to honor the wisdom of a leader who “provided unity and security in the Arabian Peninsula following centuries of fragmentation, dissension and instability.”





































